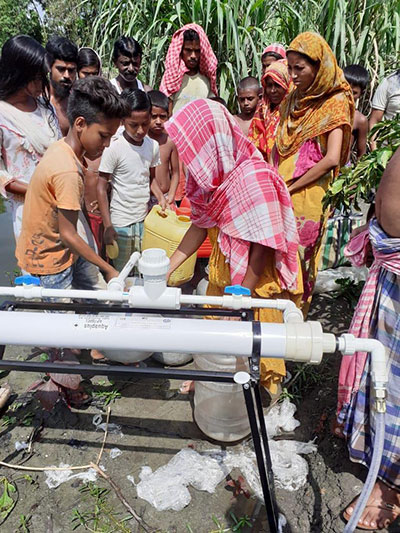
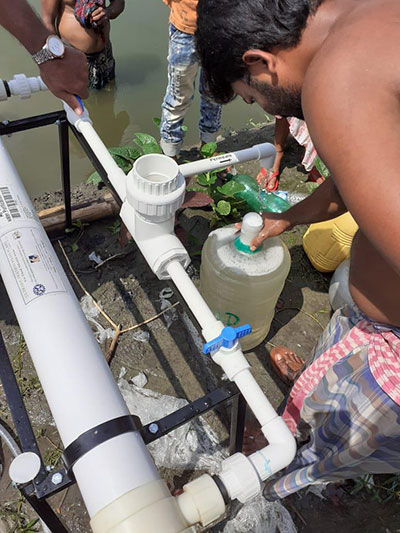
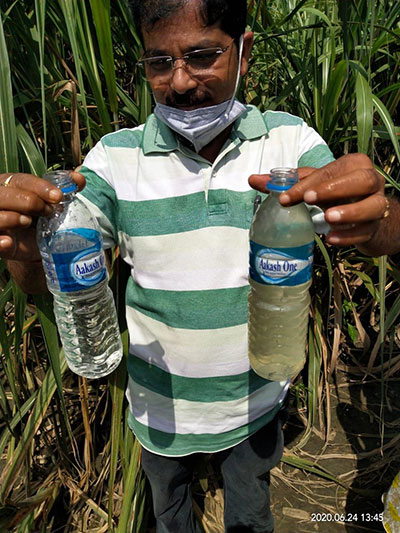
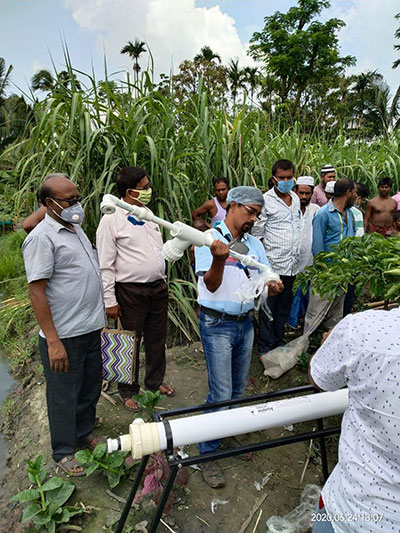
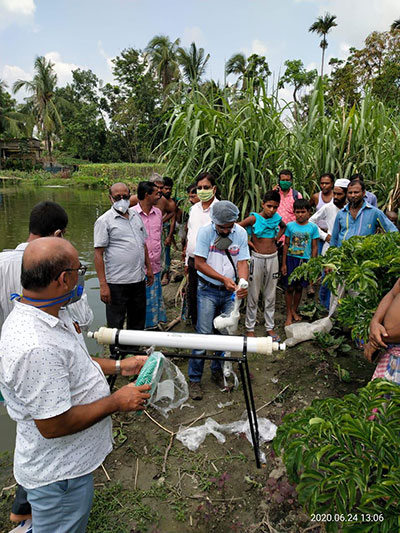
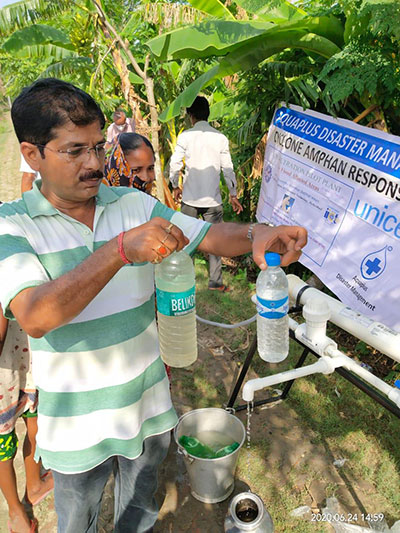
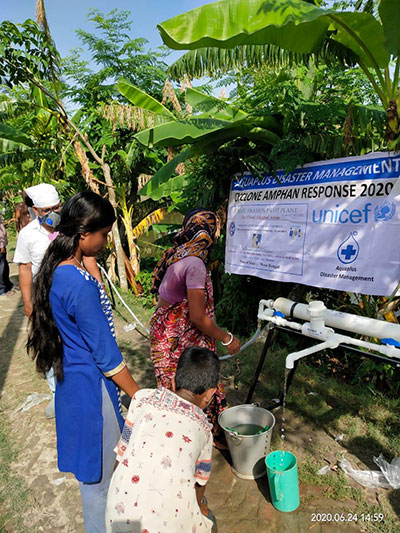
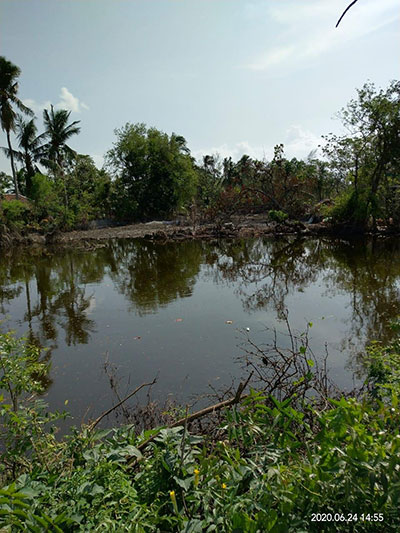
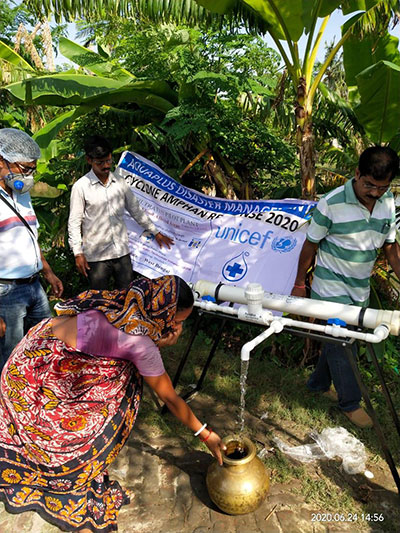
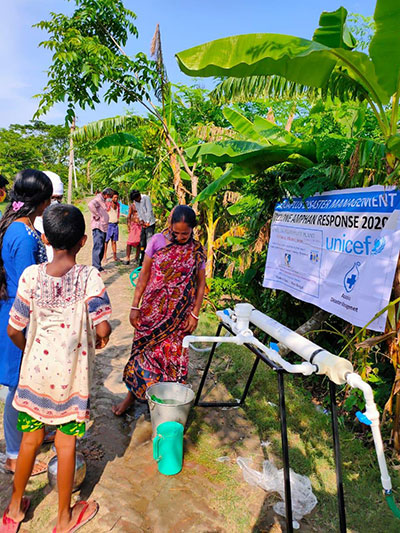
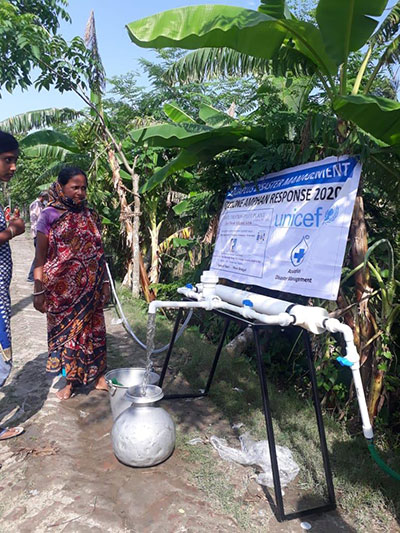
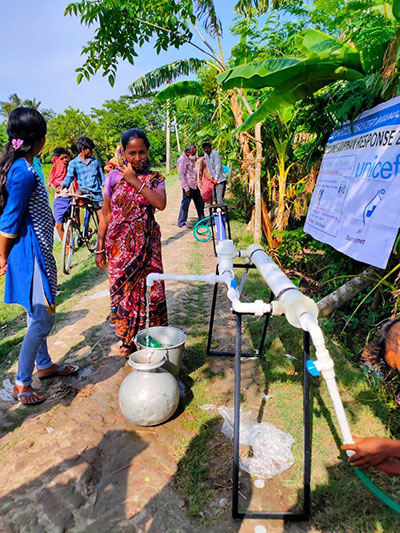
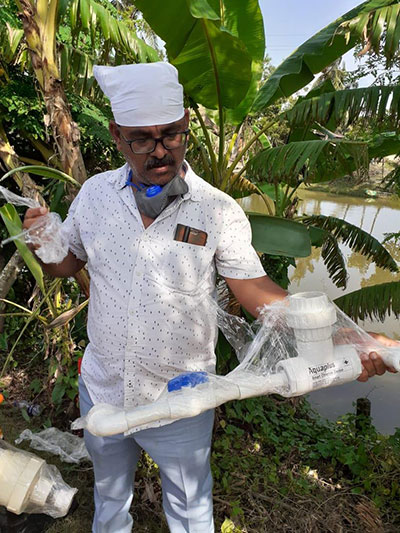
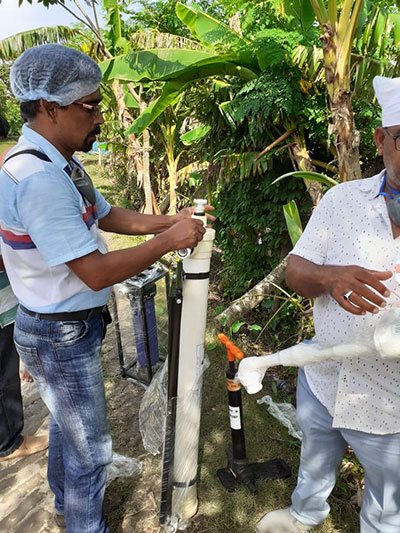
OVERVIEW
Cyclone Amphan
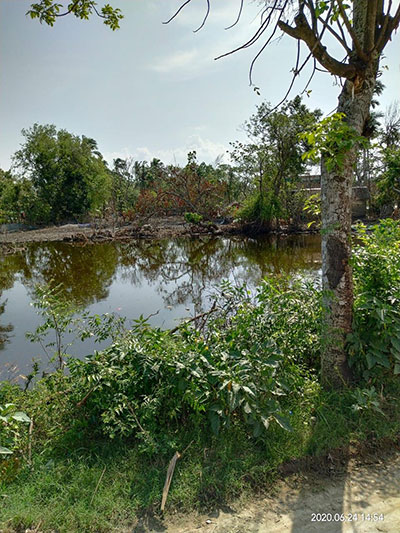
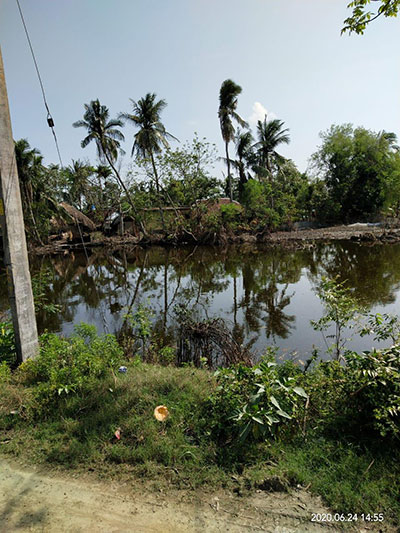
Super Cyclonic Storm Amphan was a powerful and deadly tropical cyclone that caused widespread damage in Eastern India, specifically West Bengal, and also Bangladesh in May 2020. It was the strongest tropical cyclone to strike the Ganges Delta since Sidr of the 2007 season and the first super cyclonic storm to occur in the Bay of Bengal since the 1999 Odisha cyclone. It was also the 3rd Super Cyclone that hit West Bengal since 1582, after 1737 and 1833. Causing over US$13 billion of damage, Amphan is also the costliest cyclone ever recorded in the North Indian Ocean, surpassing the record held by Cyclone Nargis of 2008.
The first tropical cyclone of the 2020 North Indian Ocean cyclone season, Amphan originated from a low-pressure area persisting a couple hundred miles (300 km) east of Colombo, Sri Lanka, on 13 May 2020. Tracking northeastward, the disturbance organized over exceptionally warm sea surface temperatures; the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) upgraded the system to a tropical depression on 15 May while the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) followed suit the following day. On 17 May, Amphan underwent rapid intensification and became an extremely severe cyclonic storm within 12 hours.
On 18 May, at approximately 12:00 UTC, Amphan reached its peak intensity with 3-minute sustained wind speeds of 240 km/h (150 mph), 1-minute sustained wind speeds of 260 km/h (160 mph), and a minimum central barometric pressure of 920 mbar (27.17 inHg). The storm began an eyewall replacement cycle shortly after it reached its peak intensity, but the continued effects of dry air and wind shear disrupted this process and caused Amphan to gradually weaken as it paralleled the eastern coastline of India. On 20 May, between 10:00 and 11:00 UTC, the cyclone made landfall in West Bengal. At the time, the JTWC estimated Amphan’s 1-minute sustained winds to be 155 km/h (100 mph). Amphan rapidly weakened once inland and dissipated shortly thereafter.